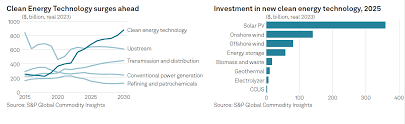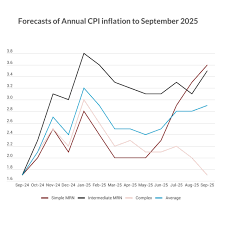
US Inflation Rate Reaches 2.7% in November, as Predicted
The US inflation rate accelerated to 2.7% in November, meeting market expectations. This marks a slight increase from the previous month, but remains within the target range set by the Federal Reserve. While the rise in inflation is significant, it shows signs of stabilization after a period of high volatility. As the economy continues to recover, experts believe that this rate is manageable and reflects a return to normalcy in the broader economic environment.
This development suggests that the US economy is showing resilience despite challenges. The 2.7% inflation rate is a reminder that while inflation pressures remain, they are not as severe as in previous years. Still, it raises important questions about future monetary policies and how they may affect households and businesses.
Why Did Inflation Reach 2.7% in November?
Several factors contributed to the US inflation rate hitting 2.7% in November. Rising energy costs, especially for gas and electricity, have been a major driver of inflation this year. Additionally, supply chain disruptions and labor shortages continue to affect prices, particularly in the goods sector. However, these increases are gradually stabilizing, which could signal a more balanced economic growth moving forward.
Food prices also saw modest increases, but they were not as dramatic as in previous months. The government’s efforts to combat inflation, including interest rate adjustments by the Federal Reserve, appear to be helping to slow down the rate of price growth.
How the US Inflation Rate Affects Consumers
For consumers, the US inflation rate at 2.7% means prices are still rising, but at a slower pace than in the past few years. While this is good news for consumers in terms of purchasing power, it still means that everyday expenses such as food, transportation, and healthcare will continue to be more expensive than before. However, the fact that the inflation rate is stabilizing offers some relief compared to the double-digit inflation seen earlier.
The Federal Reserve’s actions to manage inflation, including interest rate hikes, are aimed at keeping inflation within a target range of around 2%. If inflation continues to hover around this level, it will likely lead to more stability in the economy and reduce uncertainty for both businesses and consumers.
The Federal Reserve’s Role in Managing Inflation
The US inflation rate is a key metric that the Federal Reserve monitors closely. Its role is to manage inflation through monetary policies, especially by adjusting interest rates. In response to rising inflation in previous years, the Fed raised rates to prevent the economy from overheating. These actions have helped to bring inflation down to a more manageable level.
By increasing interest rates, the Fed makes borrowing more expensive, which can slow down spending and demand. This, in turn, helps to prevent prices from rising too quickly. As of now, the 2.7% inflation rate in November signals that the Fed’s strategy is working. However, there are still concerns about the potential for inflation to rise again in the future, particularly if global economic conditions change or new disruptions occur.
Looking Ahead: Will Inflation Continue to Stabilize?
Looking ahead, the big question is whether the US inflation rate will continue to stabilize or if we will see another spike in inflation. Many economists believe that inflation will remain relatively steady in the coming months, especially as supply chain issues improve and energy prices stabilize. However, geopolitical risks, such as global supply disruptions or unforeseen events, could cause temporary inflationary spikes.
The Federal Reserve is expected to continue its cautious approach to monetary policy, adjusting interest rates as necessary to keep inflation under control. If inflation remains steady around 2.7%, it will be a sign that the economy is moving toward more sustainable growth.
Conclusion: A Positive Sign for Economic Stability
The US inflation rate reaching 2.7% in November signals that inflationary pressures are starting to stabilize after a period of significant economic disruption. While prices are still rising, the rate of increase is much slower, which offers hope for future economic stability. For consumers, this may mean more predictable prices, while businesses can also benefit from a more stable economic environment.
In the coming months, the Federal Reserve will continue to play a key role in managing inflation, ensuring that it does not rise too quickly. For now, the 2.7% inflation rate in November appears to be a positive development, pointing to a more balanced and resilient economy.